Wright State University Lake Campus/University Physics Volume 1/Equations

Template:Green WSU Lake Template:Green
Math


Metric prefixes on page 5.
Template:Clear
Template:Colbegin
▭ Arclength ▭ radius
▭ (in radians)
▭ Circumference of circle
▭ Area of circle
▭ Area of sphere
▭ Volume of sphere
▭
Mechanics
Symbols
Template:Colbegin
▭ Position
▭ Line element (better than )
▭ Velocity [m/s]
▭ Acceleration [m/s]
▭ Force [N], Mass [kg], Acceleration [m/s2]
▭ Friction force [N] or frequency [Hz=s−1]
▭ (static, kinetic) coefficient of friction
▭ normal force
▭ gravitational constant (Earth: 9.8m/s2)
Template:Green G≈Template:Val
▭ Work [J=Nm=kg(m/s)2]
▭ Power [W=J/s]
▭ Momentum
▭ Pressure (N/m2)
▭ Kinetic (Potential) Energy [J=Nm=Ws]
▭ Potential energy (gravity, spring)
▭ defines spring constant [N/m]
▭ Tension [N] or period [s] or temperature [K]
▭ Heat [J=Ws]
▭ Angle (radians)
▭ Angular velocity (speed) [s−1]
▭ Angular acceleration [s−2]
▭ Moment of inertia
▭ Torque ▭ Angular momentum
Template:Colend
Template:Clear
Kinematics
| Linear motion | Rotational motion | Defining equation |
|---|---|---|
| Displacement = | Angular displacement = | |
| Velocity = | Angular velocity = | |
| Acceleration = | Angular acceleration = | |
| Mass = | Moment of Inertia = | |
| Force = | Torque = | |
| Momentum= | Angular momentum= | |
| Kinetic energy = | Kinetic energy = |
| Vector notation | Component notation |
|---|---|
| Free fall: |
| Linear motion | Angular motion |
|---|---|
Equations
Template:Colbegin
▭
▭ ▭
▭
▭
▭ is power
▭ Momentum
▭
▭ Inelastic collision
▭ frequency-period
▭ centripetal acceleration
▭ statics
▭ friction
▭ Newtonian gravity
▭ Newtonian gravity
▭ planet's surface gravity
Template:Colend
Fluid_Mechanics

▭ Pressure
Buoyant force equals weight of the displaced fluid. If is the weight of a cylindrical object, the displaced volume is
Template:Spaces▭ and ▭
▭ Pressure vs depth/height (constant density)
Oscillations
▭ Simple harmonic motion
▭ , where and is spring constant
▭ Energy
- speed of sound (T in Kelvins). where
- Speed of a stretched string wave: is the tension and is the linear mass density (kilograms per meter).

- relates the frequency, f, wavelength, λ,and the the phase speed, vp of the wave (also written as vw) This phase speed is the speed of individual crests, which for sound and light waves also equals the speed at which a wave packet travels.
- describes the n-th normal mode vibrating wave on a string that is fixed at both ends (i.e. has a node at both ends). The mode number, n = 1, 2, 3,..., as shown in the figure.
- Beat frequency: The frequency of beats heard if two closely space frequencies, and , are played is .
- Musical acoustics: Frequency ratios of 2/1, 3/2, 4/3, 5/3, 5/4, 6/5, 8/5 are called the (just) "octave", "fifth", "fourth", "major-sixth", "major-third", "minor-third", and "minor-sixth", respectively.
Thermodynamics
Constants and conversions
- Boltzmann's constant = kB≈ Template:Nowrap, and the gas constant is R = Template:Nowrap≈Template:Nowrap, where NA≈ Template:Nowrap is the Avogadro number.
- Boltzmann's constant can also be written in eV and Kelvins: kB ≈Template:Nowrap, where Template:Nowrap begin1eV=1.602x10−19 JoulesTemplate:Nowrap end
- converts from Celsius to Kelvins, and converts from Celsius to Fahrenheit.
- 1 amu = 1 u ≈ 1.66 × 10-27 kg is the approximate mass of a proton or neutron.
13-Temperature, Kinetic Theory, and Gas Laws
- is the ideal gas law, where P is pressure, V is volume, n is the number of moles and N is the number of atoms or molecules. Temperature is in Kelvins.
- is the average translational kinetic energy per "atom" of a 3-dimensional ideal gas.
- is the root-mean-square speed of atoms in an ideal gas.
14-Heat and Heat Transfer
<section begin=14-Heat_and_Heat_Transfer/> Here it is convenient to define heat as energy that passes between two objects of different temperature The SI unit is the Joule. The rate of heat trasfer, or is "power": Template:Nowrap begin1 Watt = 1 W = 1J/sTemplate:Nowrap end
- is the heat required to change the temperature of a substance of mass, m. The change in temperature is ΔT. The specific heat, cS, depends on the substance (and to some extent, its temperature and other factors such as pressure). Heat is the transfer of energy, usually from a hotter object to a colder one. The units of specfic heat are energy/mass/degree, or Template:Nowrap beginJ/(kg-degree)Template:Nowrap end.
- is the heat required to change the phase of a a mass, m, of a substance (with no change in temperature). The latent heat, L, depends not only on the substance, but on the nature of the phase change for any given substance. LF is called the latent heat of fusion, and refers to the melting or freezing of the substance. LV is called the latent heat of vaporization, and refers to evaporation or condensation of a substance.
- is rate of heat transfer for a material of area, A. The difference in temperature between two sides separated by a distance, d, is . The thermal conductivity, kc, is a property of the substance used to insulate, or subdue, the flow of heat.
15-Thermodynamics

- Here, Pressure (P), Energy (E), Volume (V), and Temperature (T) are the state functions.

- The net work done per cycle is the area enclosed by the loop and equals the net heat flow into the system, (valid only for closed loops).
- is the work done on a system of pressure P by a piston of voulume V. If ΔV>0 the substance is expanding as it exerts an outward force, so that ΔW<0 and the substance is doing work on the universe; ΔW>0 whenever the universe is doing work on the system.
- is the amount of heat (energy) that flows into a system. It is positive if the system is placed in a heat bath of higher temperature. If this process is reversible, then the heat bath is at an infinitesimally higher temperature and a finite ΔQ takes an infinite amount of time.
- is the change in energy (First Law of Thermodynamics).
- is work done on system. is work (out) per cycle.
Original (long) formula sheet
{{#lst:OpenStax University Physics Volume 1/Equations (master)|Introduction}}
- Template:Green and the circle's area is is its area.
- The surface area of a sphere is and sphere's volume is
- Template:Green = .621 miles and 1 MPH = 1 mi/hr ≈ .447 m/s
- Template:Green is 1.2kg/m3, with pressure 105Pa. The density of water is 1000kg/m3.
- Template:GreenTemplate:Val
- Template:Green = G ≈ Template:Val
- Template:Green = c ≈ 3×108m/s
- Template:Green
- Template:Green.... <These 8 equations were added for WSU-L exams>
{{#lst:OpenStax University Physics Volume 1/Equations (master)|Units_and_Measurement}} {{#lst:OpenStax University Physics Volume 1/Equations (master)|Vectors}} {{#lst:OpenStax University Physics Volume 1/Equations (master)|Motion_Along_a_Straight_Line}} {{#lst:OpenStax University Physics Volume 1/Equations (master)|Motion_in_Two_and_Three_Dimensions}}
| Template:Spaces | Template:Spaces | |
| Template:Spaces | Template:Spaces |
...in advanced notation this becomes .
In free fall we often set, ax=0 and ay= -g. If angle is measured with respect to the x axis:
Template:Spaces Template:Spaces Template:Spaces
{{#lst:OpenStax University Physics Volume 1/Equations (master)|Newton's_Laws_of_Motion}}

{{#lst:OpenStax University Physics Volume 1/Equations (master)|Applications_of_Newton's_Laws}}
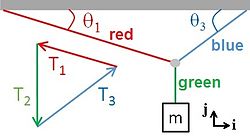
- ,
- ,
- ,
- relates the radian, degree, and revolution.
- is the number of revolutions per second, called frequency.
- is the number of seconds per revolution, called period. Obviously .
- is called angular frequency (ω is called omega, and θ is measured in radians). Obviously
- is the acceleration of uniform circular motion, where v is speed, and r is radius.
- , where T is period.
{{#lst:OpenStax University Physics Volume 1/Equations (master)|Work_and_Kinetic_Energy}} {{#lst:OpenStax University Physics Volume 1/Equations (master)|Potential_Energy_and_Conservation_of_Energy}} {{#lst:OpenStax University Physics Volume 1/Equations (master)|Linear_Momentum_and_Collisions}} {{#lst:OpenStax University Physics Volume 1/Equations (master)|Fixed-Axis_Rotation}} {{#lst:OpenStax University Physics Volume 1/Equations (master)|Angular_Momentum}} {{#lst:OpenStax University Physics Volume 1/Equations (master)|Static_Equilibrium_and_Elasticity}} {{#lst:OpenStax University Physics Volume 1/Equations (master)|Gravitation}} {{#lst:OpenStax University Physics Volume 1/Equations (master)|Fluid_Mechanics}} {{#lst:OpenStax University Physics Volume 1/Equations (master)|Oscillations}} {{#lst:OpenStax University Physics Volume 1/Equations (master)|Waves}}
Pressure and displacement fluctuations in a sound wave and
▭ Speed of sound in a fluid , ▭ in a solid , ▭ in an idal gas , ▭ in air
{{#lst:Physics_equations/Equations|17-Physics_of_Hearing}}

- relates the frequency, f, wavelength, λ,and the the phase speed, vp of the wave (also written as vw) This phase speed is the speed of individual crests, which for sound and light waves also equals the speed at which a wave packet travels.
- describes the n-th normal mode vibrating wave on a string that is fixed at both ends (i.e. has a node at both ends). The mode number, n = 1, 2, 3,..., as shown in the figure.
- Beat frequency: The frequency of beats heard if two closely space frequencies, and , are played is .
- Musical acoustics: Frequency ratios of 2/1, 3/2, 4/3, 5/3, 5/4, 6/5, 8/5 are called the (just) "octave", "fifth", "fourth", "major-sixth", "major-third", "minor-third", and "minor-sixth", respectively.
- converts from Celsius to Kelvins, and converts from Celsius to Fahrenheit.
- is the ideal gas law, where is pressure, is volume, is the number of moles and is the number of atoms or molecules. Temperature must be measured on an absolute scale (e.g. Kelvins).
- Boltzmann's constant = ≈ Template:Nowrap, and the gas constant is ≈Template:Nowrap, where ≈ Template:Nowrap is the Avogadro number. Boltzmann's constant can also be written in eV and Kelvins: kB ≈Template:Nowrap.
- is the average translational kinetic energy per "atom" of a 3-dimensional ideal gas.
- is the root-mean-square speed of atoms in an ideal gas.
- is the total energy of an ideal gas, where only if the gas is monatomic.
{{#lst:Physics_equations/Equations|15-Thermodynamics}}